Cassandra database
CASSANDRA DATABASE
Cassandra is a distributed database management system which is open source with wide column store, NoSQL database to handle large amount of data across many commodity servers which provides high availability with no single point of failure. It is written in Java and developed by Apache Software Foundation.
Avinash Lakshman & Prashant Malik initially developed the Cassandra at Facebook to power the Facebook inbox search feature. Facebook released Cassandra as an opensource project on Google code in July 2008. In March 2009 it became an Apache Incubator project and in February 2010 it becomes a top-level project. Due to its outstanding technical features Cassandra becomes so popular.
Apache Cassandra is used to manage very large amounts of structure data spread out across the world. It provides highly available service with no single point of failure. Listed below are some points of Apache Cassandra:
- It is scalable, fault-tolerant, and consistent.
- It is column-oriented database.
- Its distributed design is based on Amazon’s Dynamo and its data model on Google’s Big table.
- It is Created at Facebook and it differs sharply from relational database management systems.
Cassandra implements a Dynamo-style replication model with no single point of failure but its add a more powerful “column family” data model. Cassandra is being used by some of the biggest companies such as Facebook, Twitter, Cisco, Rackspace, eBay, Netflix, and more.
The design goal of a Cassandra is to handle big data workloads across multiple nodes without any single point of failure. Cassandra has peer-to-peer distributed system across its nodes, and data is distributed among all the nodes of the cluster.
All the nodes of Cassandra in a cluster play the same role. Each node is independent, at the same time interconnected to other nodes. Each node in a cluster can accept read and write requests, regardless of where the data is actually located in the cluster. When a node goes down, read/write request can be served from other nodes in the network.
Features of Cassandra:
Cassandra has become popular because of its technical features. There are some of the features of Cassandra:
- Easy data distribution –
It provides the flexibility to distribute data where you need by replicating data across multiple data centers.
for example:
If there are 5 node let say N1, N2, N3, N4, N5 and by using partitioning algorithm we will decide the token range and distribute data accordingly. Each node have specific token range in which data will be distribute. let’s have a look on diagram for better understanding. - Flexible data storage –
Cassandra accommodates all possible data formats including: structured, semi-structured, and unstructured. It can dynamically accommodate changes to your data structures accordingly to your need. - Elastic scalability –
Cassandra is highly scalable and allows to add more hardware to accommodate more customers and more data as per requirement. - Fast writes –
Cassandra was designed to run on cheap commodity hardware. Cassandra performs blazingly fast writes and can store hundreds of terabytes of data, without sacrificing the read efficiency. - Always on Architecture –
Cassandra has no single point of failure and it is continuously available for business-critical applications that can’t afford a failure. - Fast linear-scale performance –
Cassandra is linearly scalable therefore it increases your throughput as you increase the number of nodes in the cluster. It maintains a quick response time. - Transaction support –
Cassandra supports properties like Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability (ACID) properties of transactions.
Cassandra powers online services and mobile backend for some of the world’s most recognizable brands, including Apple, Netflix, and Facebook.
Architecture of Apache Cassandra:
In this section we will describe the following component of Apache Cassandra.Basic Terminology:
Data center Cluster
Operations:
Read Operation Write Operation
Storage Engine:
CommitLog Memtables SSTables
Data Replication Strategies
let’s discuss one by one.
Basic Terminology:
1. Node:
Node is the basic component in Apache Cassandra. It is the place where actually data is stored. For Example:As shown in diagram node which has IP address 10.0.0.7 contain data (keyspace which contain one or more tables).
Figure – Node
2. Data Center:
Data Center is a collection of nodes.
For example:DC – N1 + N2 + N3 …. DC: Data Center N1: Node 1 N2: Node 2 N3: Node 3
3. Cluster:
It is the collection of many data centers.
For example:C = DC1 + DC2 + DC3…. C: Cluster DC1: Data Center 1 DC2: Data Center 2 DC3: Data Center 3

Figure – Node, Data center, Cluster
Operations:
1. Read Operation:
In Read Operation there are three types of read requests that a coordinator can send to a replica. The node that accepts the write requests called coordinator for that particular operation.- Step-1: Direct Request:
In this operation coordinator node sends the read request to one of the replicas. - Step-2: Digest Request:
In this operation coordinator will contact to replicas specified by the consistency level. For Example: CONSISTENCY TWO; It simply means that Any two nodes in data center will acknowledge. - Step-3: Read Repair Request:
If there is any case in which data is not consistent across the node then background Read Repair Request initiated that makes sure that the most recent data is available across the nodes.
2. Write Operation:
- Step-1:
In Write Operation as soon as we receives request then it is first dumped into commit log to make sure that data is saved. - Step-2:
Insertion of data into table that is also written in MemTable that holds the data till it’s get full. - Step-3:
If MemTable reaches its threshold then data is flushed to SS Table.

Figure – Write Operation in Cassandra
Storage Engine:
- Commit log:
Commit log is the first entry point while writing to disk or memTable. The purpose of commit log in apache Cassandra is to server sync issues if a data node is down. - Mem-table:
After data written in Commit log then after that data is written in Mem-table. Data is written in Mem-table temporarily. - SSTable:
Once Mem-table will reach a certain threshold then data will flushed to the SSTable disk file.
Data Replication Strategy:
Basically it is used for backup to ensure no single point of failure. In this strategy Cassandra uses replication to achieve high availability and durability. Each data item is replicated at N hosts, where N is the replication factor configured \per-instance”.There are two type of replication Strategy: Simple Strategy, and Network Topology Strategy. These are explained as following below.
1. Simple Strategy:
In this Strategy it allows a single integer RF (replication_factor) to be defined. It determines the number of nodes that should contain a copy of each row. For example, if replication_factor is 2, then two different nodes should store a copy of each row. It treats all nodes identically, ignoring any configured datacenters or racks.CQL(Cassandra Query language) query for Simple Strategy. A keyspace is created using a CREATE KEYSPACE statement:
create_keyspace_statement ::= CREATE KEYSPACE [ IF NOT EXISTS ] keyspace_name WITH optionsFor instance:
CREATE KEYSPACE User_data WITH replication = {'class': 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor' : 2};To check keyspace Schema used the following CQl query.
DESCRIBE KEYSPACE User_data
Pictorial Representation of Simple Strategy.

Figure – Simple Strategy
2. Network Topology Strategy:
In this strategy it allows a replication factor to be specified for each datacenter in the cluster. Even if your cluster only uses a single datacenter. This Strategy should be preferred over SimpleStrategy to make it easier to add new physical or virtual datacenters to the cluster later.CQL(Cassandra Query language) query for Network Topology Strategy.
CREATE KEYSPACE User_data WITH replication = {'class': 'NetworkTopologyStrategy', 'DC1' : 2, 'DC2' : 3} AND durable_writes = false;To check keyspace Schema used the following CQl query.
DESCRIBE KEYSPACE User_data
Pictorial Representation of Network Topology Strategy.

Figure – Network Topology Strategy
Table Structure in Cassandra:
USE User_data; CREATE TABLE User_table ( User_id int, User_name text, User_add text, User_phone text, PRIMARY KEY (User_id) ); Insert into User_data (User_id, User_name, User_add, User_phone ) VALUES(1000, ‘Ashish’, ‘Noida’, ‘8077178539’); Insert into User_data (User_id, User_name, User_add, User_phone ) VALUES(1001, ‘Ashish Gupta’, ‘Bangalore’); Insert into User_data (User_id, User_name, User_add, User_phone ) VALUES(1002, ‘Abi’);Output:
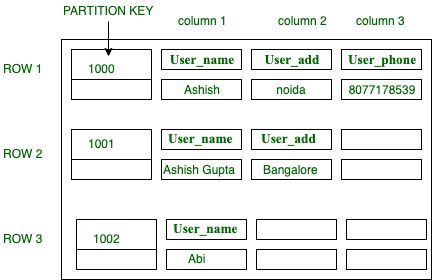
Figure – Table Structure
Application of Apache Cassandra:
Some of the application use cases that Cassandra excels in include:- Real-time, big data workloads
- Time series data management
- High-velocity device data consumption and analysis
- Media streaming management (e.g., music, movies)
- Social media (i.e., unstructured data) input and analysis
- Online web retail (e.g., shopping carts, user transactions)
- Real-time data analytics
- Online gaming (e.g., real-time messaging)
- Software as a Service (SaaS) applications that utilize web services
- Online portals (e.g., healthcare provider/patient interactions)
- Most write-intensive systems
- Step-1: Direct Request:


Comments
Post a Comment